-
ceo.bfi@gmail.com
Send Email
-
2C, C-6/A Block, Janakpuri, Delhi India 110058
Visit Our Office
99902-92279
Confidentiality Guaranteed
99902-92279
Confidentiality Guaranteed

Nov
DNA Fingerprinting
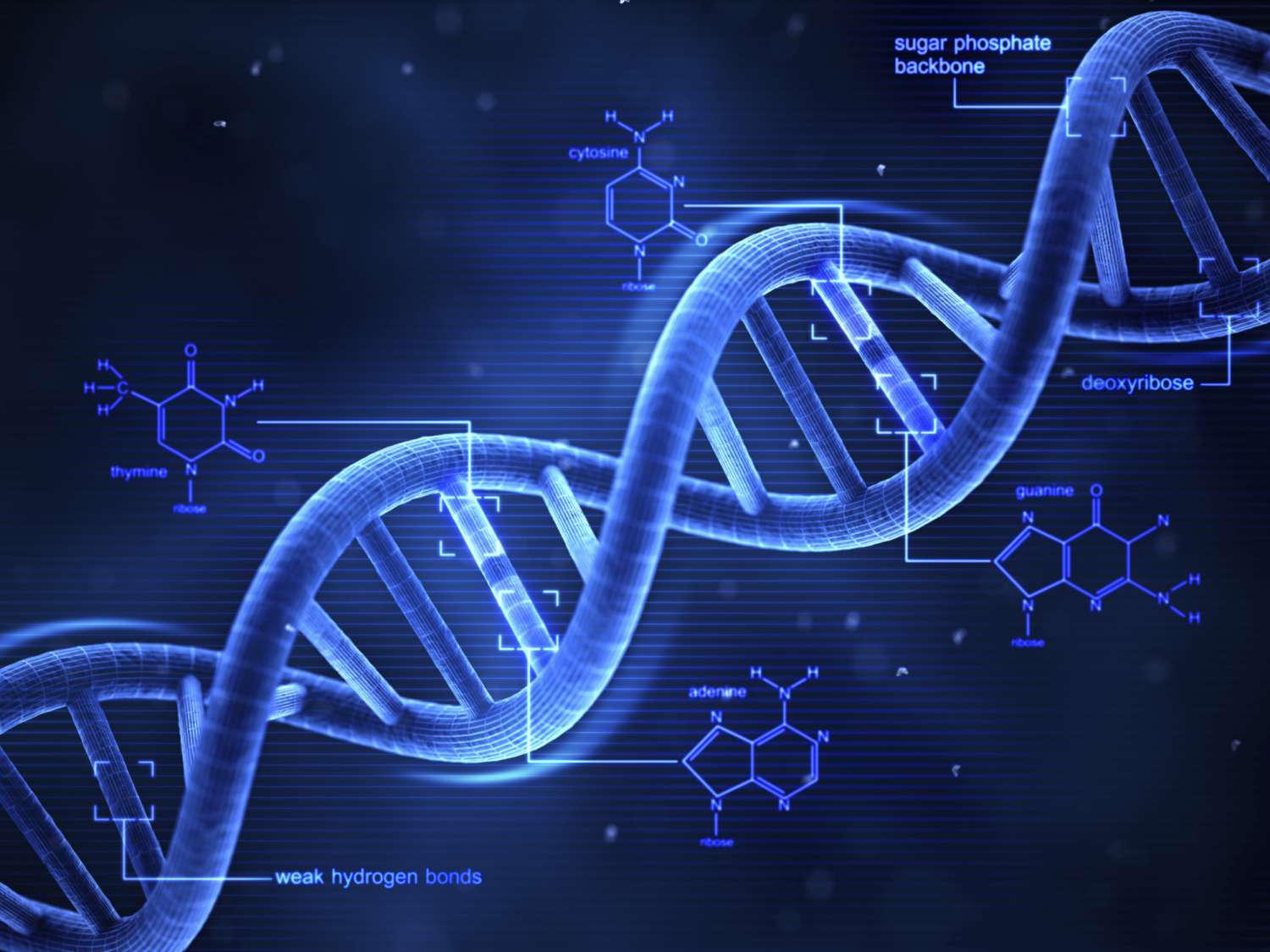
DNA fingerprinting is the scientific method of analyzing the short tandem repeats (STRs) in a person’s DNA. These regions vary significantly from individual to individual, making them ideal for identity verification. Except for identical twins, every human has a unique DNA profile.
The process involves collecting biological samples (blood, hair, saliva, semen, skin), extracting DNA, amplifying specific regions using Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), and then comparing these regions for similarities or differences.
In today’s high-tech world of forensic science, no tool is as definitive and reliable as DNA fingerprinting. Also known as DNA profiling or genetic fingerprinting, this cutting-edge technique allows forensic experts to identify individuals with extraordinary precision based on their unique genetic code.
At Brilliant Forensic Investigation, we utilize state-of-the-art DNA analysis technologies to assist law enforcement, legal professionals, and private clients in uncovering the truth. Whether it’s a complex criminal case, a paternity dispute, or an unidentified body, DNA fingerprinting remains an essential pillar of modern forensic services.
Key Steps in the DNA Fingerprinting Process
Sample Collection:
Biological evidence like blood stains, saliva on envelopes, cigarette butts, hair strands with follicles, or skin under fingernails is collected from the crime scene.
DNA Extraction:
The sample is processed in a controlled laboratory setting to isolate the DNA molecules.
PCR Amplification:
Specific sections of DNA, particularly STRs, are amplified to produce enough data for comparison.
Gel Electrophoresis or Capillary Electrophoresis:
This separates DNA fragments based on size to generate a DNA profile.
Profile Comparison:
The resulting DNA profile is compared against suspect samples or existing databases like CODIS (in countries where applicable).
Criminal Investigations
DNA profiling is vital in identifying perpetrators in rape, murder, burglary, and assault cases. Even a single drop of blood or strand of hair can link a suspect to the crime scene.
Paternity and Relationship Testing
DNA analysis can establish or deny biological relationships in cases of child custody, inheritance, and immigration.
Identification of Decomposed or Unidentified Bodies
When physical identification is impossible, DNA helps identify victims of mass disasters, accidents, or long-unsolved missing person cases.
Wildlife Forensics
Used to track poaching, illegal animal trade, or determine the species from biological traces.
Exoneration and Appeals
Wrongfully convicted individuals have been exonerated through post-conviction DNA testing, reshaping the justice system globally.
Why DNA Fingerprinting Is Legally Significant
In courts of law, DNA evidence is often considered conclusive and scientifically valid, provided the chain of custody and handling protocols are strictly followed.
At Brilliant Forensic Investigation, our DNA profiling reports are:
Prepared by qualified forensic DNA experts
Admissible in courts across jurisdictions
Compliant with legal and scientific standards
Delivered with expert testimony support if needed
Real-World Case Examples
Nirbhaya Case (India, 2012)
Case Background:
On the night of December 16, 2012, a brutal gang rape and assault took place on a 23-year-old physiotherapy intern in Delhi, later known publicly as “Nirbhaya.” The horrific nature of the crime sparked nationwide outrage and brought significant reforms to Indian laws concerning sexual violence.
Forensic Role and DNA Fingerprinting:
In this case, DNA evidence was central to proving the guilt of the accused. The victim’s blood, along with biological evidence collected from her clothes and body during the medical examination, was preserved for forensic analysis. Vaginal swabs and other internal samples were tested.
Semen samples found on the victim matched the DNA profiles of the six accused men.
Blood traces found on the bus, clothes of the accused, and on the iron rod used in the attack were matched using DNA fingerprinting techniques.
The Delhi Forensic Science Laboratory (DFSL) employed advanced PCR techniques to generate the DNA profiles, linking each accused to the crime scene.
Outcome:
The matching DNA evidence proved critical in securing convictions. The fast-track court awarded death sentences, later upheld by higher courts, with four of the accused executed in 2020. The scientific credibility of DNA fingerprinting in this case set a precedent for handling sexual assault cases in India.
Rajiv Gandhi Assassination Case (1991)
Case Background:
On May 21, 1991, former Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi was assassinated in Sriperumbudur, Tamil Nadu, by a female suicide bomber from the Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE). The blast killed 14 others and left many injured. The suicide attack created chaos, with multiple bodies badly mutilated and difficult to identify.
Forensic Role and DNA Fingerprinting:
The forensic challenge in this case was to identify the human remains of the suicide bomber among the dismembered bodies at the explosion site.
Investigators recovered the detached head of a woman that did not match any of the local victims.
The Tamil Nadu Forensic Sciences Department extracted DNA from the head and compared it with suspected LTTE operatives’ profiles using early forms of DNA profiling.
Additionally, clothing fragments and other personal items were examined for biological residues, helping to reconstruct the chain of events and confirm the attacker’s identity.
Outcome:
This forensic breakthrough helped establish that the attack was executed by Thenmozhi Rajaratnam (also known as Dhanu), an LTTE operative. The identification strengthened the investigative leads and confirmed the LTTE’s direct involvement. The case became one of the first high-profile uses of DNA fingerprinting in political assassinations in India.
Indian Ocean Tsunami Victim Identification (2004)
Case Background:
On December 26, 2004, a massive undersea earthquake off the coast of Sumatra triggered a devastating tsunami, claiming over 230,000 lives across multiple countries, including India, Sri Lanka, Thailand, and Indonesia. Thousands of victims were swept away, and their bodies were recovered in severely decomposed states.
Forensic Role and DNA Fingerprinting:
In the wake of the disaster, identifying the deceased—especially foreigners and displaced local populations—became a monumental humanitarian task.
The International Commission on Missing Persons (ICMP), along with national forensic teams, used DNA fingerprinting to identify the remains.
Teeth, bones, and preserved tissue were used as DNA sources in cases of extreme decomposition.
Where traditional identification methods (e.g., facial recognition or fingerprinting) failed, DNA profiles were matched against samples provided by families of the missing (like toothbrushes, hairbrushes, or buccal swabs).
In India, the Central Forensic Science Laboratory (CFSL) and other agencies collaborated to process mass DNA evidence in Tamil Nadu and Andaman & Nicobar Islands.
Outcome:
DNA analysis enabled the identification of thousands of tsunami victims, ensuring proper burials and providing closure to grieving families. The initiative also set the groundwork for disaster victim identification (DVI) protocols using DNA in mass casualty events worldwide.
Call To Action

Are you interested in learning more about forensic expert or seeking professional forensic-expert services? Contact us today to inquire about our expertise.
📞 Contact Us: 9990292279
🌐 Visit Our Website: https://forensicexpertinvestigation.com/
✉️ Email: ceo.bfi@gmail.com




